ऊतक (TISSUES)
- कोशिकाओं के समूह को ऊतक कहते है जो एक विशिस्ट कार्य को सम्पादन करता है।
- जैसे पेशिये कोशिका सिकुड़ने तथा फैलने का कार्य करती है।
- तंत्रिका कोशिकाएं सन्देश को वाहक करने में।
- रक्त, हार्मोन, भोजन, ऑक्सीजन और अपशिस्ट प्रदार्थ का वहन करने के लिए।
- पौधों में वाहक नलिकाए संम्ब्धित कोशिकाए भोजन तथा जल का परिवाहन करता है।
- बहु-कोशिकीय जीवो में श्रम विभान होता है।
पौधों में सहारा मृत कोशिका के द्वारा होता है तथा पौधों के विभाजन क्षमता के अनुसार ही पौधे के UTAK को वर्गीकरण किया जाता है।
- जन्तुओ में कोशिका वृद्धि अधिक एकरुप होती है इसीलिए जन्तुओ में विभाज्य तथा अविभाज्य क्षेत्रो की कोई सिमा नहीं होती है।
पादप उत्तंक (padak utak)
-
पौधों में एक निश्चित क्षेत्रो में होती है इसका कारण विभज्योतक कहलाता है।
-
विभज्योतक की कोशिकाए अत्यधिक क्रियाये होती है तथा अत्यधिक कोशकाये द्रव्य पतली कोशिका भित्ति और स्पष्ट केन्द्रकऔर इसमें रसधानी नहीं होती है।
स्थयी ऊतक
- विभज्योतक कोशिका द्वारा बनी UTAKअपना शक्ति खो देता है जिसके परिणाम स्वरूप स्थायी ऊतक का निर्माण होता है।
-
एक विशिस्ट कार्य करने के लिए स्थायी रूप और आकर लेने की क्रिया को विभेदीकरण कहते है।
स्थायी ऊतक दो प्रकार का होता है
सरल स्थयी ऊतक
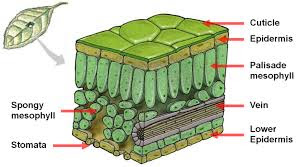
- एपिडर्मिस ऊतक के निचे वाले परत को सरल स्थाई ऊतक कहते है। पैरेंकारमा इसमें अधिक पाया जाने बाला ऊतक है इसमें रिक्तया ज्यादा होता है दो कोशिकाओं के बिच।
-
ये भोजन भंडारण करता है कुछ पैरेन्काइमा ऊतकों में क्लोरोफिल पाया जिससे प्रकाश संश्लेषण सम्पादन होता है उसे जकीरेबजौना कहा जाता है।
-
जलिए पौधों में पैरेन्काइमा की कोशिकाओं के मध्य हवा की गुटिकाऐं पायी जाती है इसे इस पैरेन्काइमा को ऐरेन्काइमा कहा जाता है।
-
पौधों में लचीलापन बिना टूटे कलेन्काइमा के कारण तथा यांत्रिक सहायता प्रदान करता है।
-
इस ऊतक की कोशिकाये जीवित, लम्बी तथा अनियमित ढंग से होता है तथा कोने में मोटी होती है।
-
इसमें रिक्तिया दो कोशिकाओं के बिच कम होता है।
स्क्लेरेन्काइमा
- यह ऊतक पौधों को कठोर और मजबूती प्रदान करती है। जैसे :- नरियल का छिलका।
- ये मृत कोशिका का पतली तथा लम्बी ऊतक होती है जिसका कारण इस ऊतक के भिंती लिगिनन के कारण मोती होती है।
- इसमें भी रिक्तिया नहीं होती है यह संवहन मंडल के निकट तथा पन्तो के शिराओ और बीजो और फ्लो के कठोर छिलके में उपस्थ्ति रहता है। कोशिका के बहरी परत एपिडर्मिस है। शुष्क स्थानों पर एपिडर्मिस मोटी होती है जो जल को बर्वाद (क्षय) से रोकती है सभी पौधों मे रक्षा प्रदान करता है।
एपिडर्मल
- यह जल को क्षय तथा यांत्रिक घात, परजीवी कवक के प्रवेश से रोकती है।
-
ये एपिडर्मिस का उत्तरदायित्व है।
-
पतियों में एपिडर्मिस में छोटे- छोटे छिद्रो को देख सकते है जिसे स्टोमेटा कहते है।
-
स्ट्रॉमेटा को दो वृक्क के जैसा संरचना से घेरे रहता है जिसे रक्षि कोशिका कहते है। स्ट्रॉमेटा द्वारा गैसों का आदान – प्रदान होता है।
-
आयु के साथ वृक्ष की सुरक्षात्मक ऊतकों में परिवर्तन होता है।
-
सुबरिन प्रदार्थ के कारण इन छालो में हवा पानी अभेद बनती है।
-
एक ही प्रकार के कोशिकाओं से निर्मित भिन्न -भिन्न प्रकार के ऊतक जो दिखने में एक समान दिखती है उसे सरल स्थायी ऊतक कहते है।
जटिल स्थायी ऊतक
-
एक से अधिक प्रकार के कोशकाओ से मिलकर बने ऊतक को स्थायी ऊतक कहते है। जैसे :- फ्लोएम, जाइलम अदि।
-
जाइलम ,फ्लोएम ऊतक को संवहन उतक भी कहते है जो संवहन मंडल का निर्माण करता है।
- जाइलम टैकिड (वाहिनिका), वाहिका, जाइलम पैरेन्काइमा और जाइलम रेशा से मिलकर बना होता है।
-
ट्रैंकिङ एवं वाहिका की कोशिका मोटीहै।
-
ट्रैंकिङ बहिकाओ की संरचना नलिकाकार होता है जिसके द्वारा खनिज लवण उधर्व्धार संवहन करता है।
-
पैरेन्काइमा भोजन संग्रह करता है जाइलम फाइवर इसे सहारा देने का कार्य करता है।
- फ्लोएम पांच प्रकार का होता है।
- फ्लाोएम पैरेन्काइमा,साथी कोशकाए, चालिनी कोशिकाए, चालनी नलिकाए, फ्लाएम रेशे आदि।
-
चलनी नलिका छिद्रित नलिकाकार होता है।
- फ्लाएम रेशो को छोड़कर फ्लोएम कोशिए जीवित कोशिकाए है।

Wow too good
Good