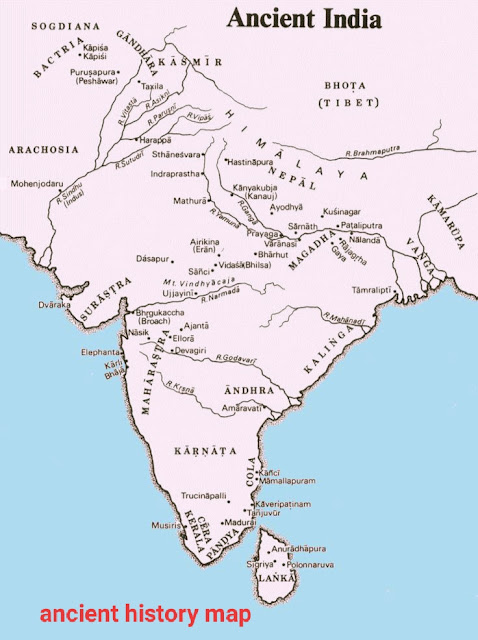
भारतीय इतिहास के स्रोत (Bharat ka itihas ke mukhya srot)
भारतीय इतिहास के स्रोत में प्राथमिक स्रोत
द्वितीयक स्रोत
भारतीय इतिहास के स्रोत में द्वितीयक स्रोत किसी और द्वारा व्यक्तियों लोगो, घटनाओ और स्थानों का बाद में दिया गया विवरण होता है। यह अप्रत्यक्ष स्रोत होता है। ये प्राथमिक स्रोत के संश्लेषण, व्याख्याव मूलयांकन करते है। शिलालेख तथा अभिलेख में अंतर क्या है। शिलालेख तथा अभिलेख भारतीय इतिहास के स्रोत से प्राथमिक स्रोत है ऐसा माना जाता है मौर्य वंश के शासक अशोक द्वारा ३३ अभिलेखों मिले।
अशोक ने अपने शासन काल पत्थर, स्तम्भ और गुफाओ में खुदबाये। वे लेख जिनको किसी खुले हुए स्थान पर पत्थर पर उत्कीर्ण किया जाता था। शिला मतलब सिल यानी एक तरह से चौकार आकर के श्यामपट्ट की आकर की तरह होता है। जिसपर आज भी हम लिखते हैं लेकिन वे लेख भविष्य काल तक विचारों व विचारधारा को सरक्षित करने के लिए लिखे जाते थे।
पुरातत्वविज्ञान:
भारतीय इतिहास के पुरातात्विक स्रोत क्या है?
-
अभिलेख
-
भूमि अनुदान पत्र
-
मुद्राए
-
स्मारक एवं भवन
-
मूर्तियां
-
चित्रकला
-
उत्खनन में प्राप्त अन्य सामग्री
भारतीय इतिहास के स्रोत में अभिलेख
भारतीय इतिहास के स्रोत में अभिलेख अनेक प्रकार के होते है जो निम्नलिखित है।
अन्य भारतीय इतिहास के स्रोत महत्वपूर्ण अभिलेख निम्नलिखित है।
| No. | भारतीय इतिहास के स्रोत में प्रशस्ति | भारतीय इतिहास के स्रोत में अभिलेख |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | खारबेल | हाथीगुफा अभिलेख |
| 2. | शक क्षत्रप रुद्रदामन | जिरनार जूनागढ़ अभिलेख |
| 3. | सातवाहन नरेश पुलुमावी का | नाशिक गुफालेख |
| 4. | समुद्रगुप्त का हरिषेण द्वारा रचित | प्रयाग स्तम्भ |
| 5. | चालुक्य पुलकेशिन द्वितीय | ऐहोल |
भूमि अनुदान पत्र स्रोत
भारतीय इतिहास के स्रोत में मुद्राओ की भूमिका
भारतीय इतिहास के स्रोत में मूर्तिकला का भूमिका
भारतीय इतिहास के स्रोत में चित्रकला की भूमिका
भारतीय इतिहास के स्रोत in english
Sources of Indian History (Main Sources of Indian History)
Primary source
The primary source is a document or craftsman that was written or created during the surrounding time period, which includes autobiographies, memoirs, and oral histories, etc., which were later written by writers and witnesses who had their own experience—important Sources Crafts, inscriptions, coins, cave art, pottery, clothes, etc. In written sources, diarrhea, speech, manuscripts (these are called manuscripts because they are handwritten. The word manuscript is made from the Latin word menu). These are often found on palm leaves or the bark of Bale Bhuj, which grows in the Himalayas.
Secondary source
The secondary source is the subsequent description of individuals, logos, events, and locations by someone else. It is an indirect source. They evaluate the synthesis, interpretation, and interpretation of the primary source. What is the difference between an inscription and an inscription? Inscriptions and inscriptions are the primary sources of Indian history.
It is believed that 33 inscriptions were found by Ashoka, the ruler of the Mauryan dynasty. Ashoka, during his reign, engraved in stones, pillars, and caves. The inscriptions were engraved on the stone in an open place. Shila means cob, i.e., in a way, it is like the shape of a square and a black plate. On which we still write today, but those articles were written to preserve ideas and ideology till the future.
Archeology:
The term is used to study the human past with the help of physical remains. This includes everything from the remains of magnificent palaces and temples to small old things that have been thrown away as unnecessary from the daily activities of human beings, such as temples, palaces, forts, and other objects such as immortal structures, bones, pollen, pieces, coins, sculptures, and inscriptions, etc.
The many purposes of archeology are to obtain these physical remains, compile their records, analyze and classify them, And describe the forms of human behavior that inspired man to create objects.
What is the archaeological source?
- Archaeological sources are the most authentic to know the ancient Bharat itihas. Archaeological sources are as follows.
Records - Land grant letter
- Currencies
- Monuments and buildings
- Sculptures
- Painting
- Other materials found in excavations
- Records
It was engraved on stone pillars, copper panto walls, coins, and statues. The first to be read is Ashoka’s inscription, written in Prakrit, which is Muski and Datia near Raichur in Karnataka state, Madhya Pradesh. In which Ashoka’s name is Devanam Priyadarshi. Most of Asoka’s inscriptions are in Vrahlipi; they were written from left to right. James Presep (1837) was successful in reading Ashoka’s inscription. More ancient records date to the Harappan civilization of 2500 BC. Which is expressed in the pictorial script. Which have not yet been read.
There are several types of records, which are as follows.
The records were such that they summarized the economic, social, and administrative orders and necessary rules issued to the state officials and the public, such as Ashoka’s records.
The second type of inscription has ritual inscriptions in which Buddhist and Jain, Vaishnava, etc. sects had rules.
The third type is the inscription, which describes the kings’ victories but does not mention their faults. His officials wrote this. The well-known inscription in the citation is the elephant cave inscription of Kharbel.
Other important records are as follows.
No. Citation records
1. Kharbel Elephant Cave Records
2. Saka Kshatrap Rudradaman Jirnar Junagadh Records
3. Nashik cave inscription of Satvahana king Pulumavi
4. Prayag pillar of Samudragupta by Harishen
5. Chalukya Pulakeshin II Aihol
Land grant letter source
It is usually inscribed (engraved) on a copper strip. There is a description of the work related to the villages, lands, and revenue given by the kings and feudal lords to the monks, Brahmin temples, monasteries, feudal lords, and officials. They are written in Prakrit, Tamil, Sanskrit, Telugu languages. The land grant letter is received in the pre-medieval (600 to 1200 AD), which suggests that there must have been a pre-medieval feudal economy.
The role of coins in the source of Indian history
Mudras have a significant role in Indian studies. We have a history from 206 BC to 300 AD. Chuki did not have articles in its earlier postures. Signs used to be engraved on them, and then more and more signs would be made on it from which exact knowledge would not be obtained.
These injuries were called coins or punches. Trees, fish, bulls, stubborn, crescents, etc. were depicted on Buddhist coins made by stamping on metals. After which kings and gods and dates are also mentioned on it. On this basis, the dynasty history was rebuilt.
Most of the coins were received in the post-Mauryan period, made of lead, putty, bronze, copper, gold, and silver. The gold coin issued by the Kushans had a lot of purity. Speaking of the Gupta ruler, Bay issued the largest amount of gold coins.
भारतीय इतिहास के स्रोत pdf




Nice Article 👍
Good content
Nice